 Canis dingo
Canis dingo
-----------
English: Dingo
German: Dingo
French: Dingo
Spanish: Dingo
Distribution areas
------------------
The dingo is a special variety of wild
dog living in the Australian continent.
Description of the fur
----------------------
The skins are from 80 to 170 cm long.
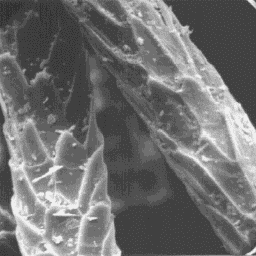
The coat occurs in different shades of The cuticular structure
yellow-brown, grey or dark-brown colour. of the fine fibres, 1000x
The belly is lighter in colour of the upper
guard hair layer and the underfur layer is only slight; the hair fibres are
straight. The longest guard hairs measure up to 45 mm.
|
|
 Canis dingo
Canis dingo
-----------
English: Dingo
German: Dingo
French: Dingo
Spanish: Dingo
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface appears furrowed. The hair
follicles are wide with sunken edges. The
average follicle contains a cluster of
hairs.
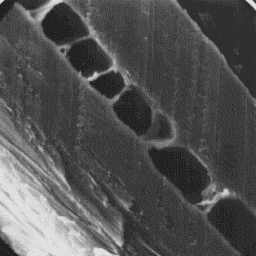
The fine fur fibres are elliptical in The cuticular structure
cross-section and are covered by of an intermediate hair, 1000x
cornet-like scales. The surface of the
cuticular scales is smooth and the scale margins are straight. These fine
fibres are non-medullated.
|
|
 Canis dingo
Canis dingo
-----------
English: Dingo
German: Dingo
French: Dingo
Spanish: Dingo
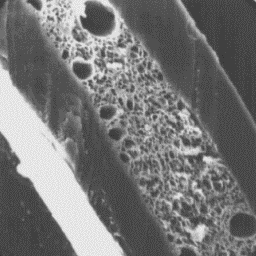
Intermediate fibres have a diameter of
20 to 35 µm. The cross-sections are
elliptical in outline, and the hair shaft
is covered by a cuticle with even,
tile-like scales at the bottom, and by the
flat-edge shaped scales in the upper part
of the shaft. The surface of the scales is
smooth and the margins are straight. The
medulla is narrow, unbroken and Longitudinal section
symmetrically situated in the central area of an intermediate fibre, 1000x
of the shafts. The overall structure of the
medulla is usually of the uniserial ladder type, but sometimes of the
lattice-sponge-like type of medulla.
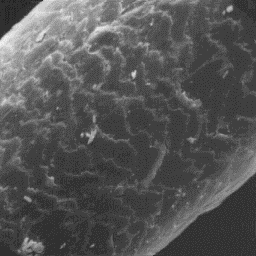
The guard hairs are circular at the bottom, but elliptical in other parts
of the hair shaft. The medulla is narrow at the bottom, but wide in the upper
part of the hair. The cuticular scales are tile-like and flat-edge shaped,
with a smooth surface and straight scale margins. The medulla is of the
lattice-sponge-like type with a foam-like infilling substance.
|
|
 Canis dingo
Canis dingo
-----------
English: Dingo
German: Dingo
French: Dingo
Spanish: Dingo
The cuticular structure
of a guard hair, 1000x
|
|
 Canis dingo
Canis dingo
-----------
English: Dingo
German: Dingo
French: Dingo
Spanish: Dingo
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 1000x
Numerical code for dingo skin structure
---------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-1-3
Fine fur fibres: 2-5-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-8.16-8.15
Intermediate fibres: 2-2.11-1-1-3-1-1-1.5-8-20.35-15.25
Guard hairs: 1.2-2.11-1-1-3.2-1-1-11-5-15.35-25.45
|




